Can You Drink Green Tea Candida Diet
Study under review: Green tea catechins prevent lowdensity lipoprotein oxidation via their accumulation in low-density lipoprotein particles in humans
Introduction
Atherosclerosis is a disease characterized by the thickening and narrowing of arterial walls due to the progressive buildup of plaque. Since atherosclerosis is a chief contributor to cardiovascular disease (CVD), the leading cause of death worldwide, there is great interest in finding ways to slow its development.
While the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis is only partially understood, mounting evidence [1] suggests that the oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) may play a pivotal role (as shown in Figure 1). Accordingly, protecting LDL from oxidation could potentially be a sound strategy in slowing its progression.
Figure 1: How oxidized LDL may contribute to athersclerosis
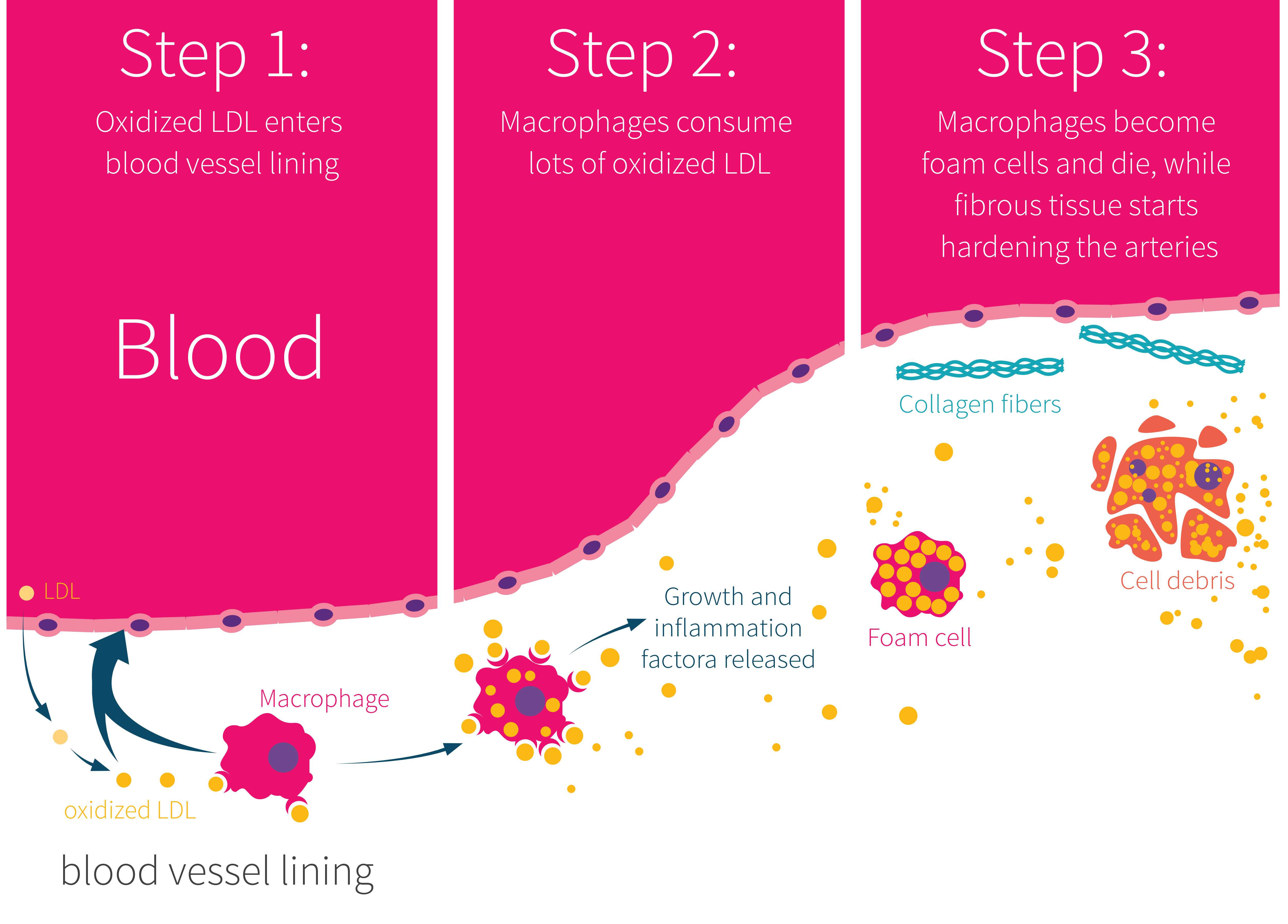
Adapted from: Stein et al.Int J Mol Sci. 2015.
A growing number of people are turning to dietary antioxidants to minimize oxidation. Lending credence to this trend, epidemiological [2] evidence [3] has displayed a positive association between use of dietary antioxidants and a reduced risk of coronary heart disease. This has been ostensibly corroborated by the results of animal studies [1] which indicate the effectiveness of antioxidants in reducing the severity of atherosclerosis. Although the few human trials [1] that exist remain equivocal, most used vitamin E or beta-carotene as their antioxidant. More clinical trials analyzing the effect of a wide range of antioxidants are needed to determine if antioxidants, either through food or supplementation, can help prevent or mitigate conditions like atherosclerosis.
Green tea is a popular beverage, in part due to its purported health benefits [4]. These health benefits may be attributed to green tea's high concentration of polyphenols, which may have antioxidant properties [5] The major type of polyphenol found in green tea are known as catechins. The four main types of catechins are epicatechin (EC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC), and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Researchers have proposed a molecular mechanism through which EGCG, the most abundant catechin in green tea, may reduce endothelial inflammation [6] by stimulating the cell's own defense system against oxidants.
Moreover, the authors of the study under review previously found [7] that directly adding green tea catechins to isolated LDL particles inhibits oxidation in a test tube (in vitro). Although these findings are promising, what happens in test tubes doesn't always replicate in humans. As a result, a few years later the authors extended their findings into humans [8], reporting that an acute intake of five grams of green tea powder led to an increase in plasma catechin levels and increased the resistance against LDL oxidation in healthy people. However, even though the increase in plasma catechin levels was simultaneous with a reduction in LDL oxidation, there was still a possibility that green tea protected LDL particles from oxidation through a mechanism unrelated to the catechins.
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to observe whether or not green tea catechins are incorporated into plasma LDL particles and thereby provide protection against LDL oxidation, both in vitro and in humans.
The oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) seems to play a pivotal part in the development of atherosclerosis, a chief contributor to cardiovascular disease (CVD). Recent studies have reported that green tea, which has a high concentration of antioxidants in the form of catechins, has the potential to reduce LDL oxidation. This study was designed to test green tea catechin incorporation into LDL particles, and hence protection against LDL oxidation.
Who and what was studied
Become an Examine Member to read the full article.
Becoming an Examine Member will keep you on the cutting edge of health research with access to in-depth analyses such as this article.
You also unlock a big picture view of 400+ supplements and 600+ health topics, as well as actionable study summaries delivered to you every month across 25 health categories.
Stop wasting time and energy — we make it easy for you to stay on top of nutrition research.
Try free for two weeks
Already a member? Please login to read this article.
What were the findings?
Become an Examine Member to unlock this article.
Already a member? Please login to read this article.
What does the study really tell us?
Become an Examine Member to unlock this article.
Already a member? Please login to read this article.
The big picture
Become an Examine Member to unlock this article.
Already a member? Please login to read this article.
Frequently Asked Questions
Become an Examine Member to unlock this article.
Already a member? Please login to read this article.
What should I know?
Become an Examine Member to unlock this article.
Free 2-week trial »
Already a member? Please login to read this article.
Can You Drink Green Tea Candida Diet
Source: https://examine.com/members/deep-dives/article/i-3-green-tea/