what does debt to equity ratio mean for a company
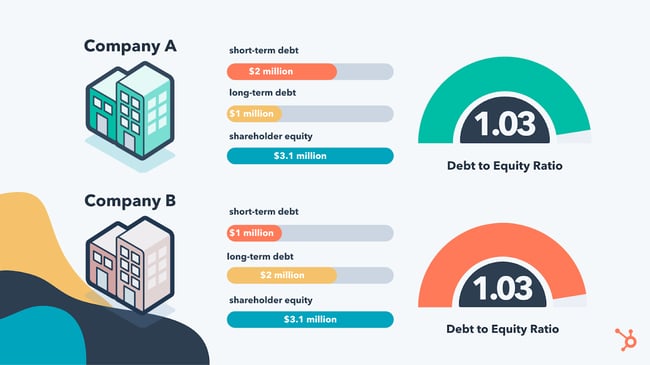
Growing a business organization requires investment majuscule. When companies are scaling, they need money to launch products, rent employees, assistance customers, and aggrandize operations. This sentiment is true now more than than ever with the collective U.S. business organisation debt to equity ratio soaring to .98 in Q1 2020 — the highest information technology'due south been since 2016. The tendency shows that businesses are growing cheers to a healthy rest of debt and equity. At that place are numerous means to raise uppercase, and each will have a different touch on your company and the step at which you abound. The most mutual way to raise capital is through either equity or debt. But what do each of these entail? And how practice they assist your business organization' fiscal standing? Well, you're in luck, considering we'll take a await in this definitive guide to demystifying the debt to equity ratio. The debt to equity ratio is a measure out of a company's fiscal leverage, and it represents the amount of debt and disinterestedness being used to finance a visitor'southward assets. It'south calculated by dividing a house's total liabilities by full shareholders' disinterestedness. Leverage is the term used to describe a business' use of debt to finance business activities and asset purchases. When debt is the primary way a company finances its business organisation, information technology'south considered highly leveraged. If it'southward highly leveraged, the debt to equity ratio tends to be higher. Information technology is important to note the debt to equity ratio will vary across industries. This is considering different types of businesses require different levels of debt and capital to operate and scale. In a LinkedIn poll conducted by Steve McNulty, Partner at Funding Nav, 34% of respondents are currently raising capital through equity, whereas the majority of those who have raised capital in the past did so through debt. Granted, this poll is express and won't speak to all businesses, merely it does give us a peek behind the financial curtain. The interesting function about McNulty's findings lies within the comments under his poll. Business organization owners aren't necessarily considering the residue betwixt these ii types of funding and what that balance looks like in their industries. Image Source For example, an dress visitor that requires textiles to create the production, labor to assemble the clothing, warehouses to shop their products, and brick-and-mortar stores to sell the product to customers is probable going to carry more debt than a tech visitor that delivers all of its products online and does not accept to worry most storing physical products or maintaining a customer-facing physical infinite. These considerations volition profoundly impact the debt to equity ratio of these 2 companies. The debt to equity ratio is a simple formula to testify how capital has been raised to run a business. It's considered an important financial metric because it indicates the stability of a company and its ability to heighten additional capital to grow. As an entrepreneur or small business concern owner, this ratio is used when applying for a loan or business line of credit. For investors, the debt to equity ratio is used to indicate how risky information technology is to invest in a company. The higher the debt to equity ratio, the riskier the investment. To further analyze the ratio, let'south ascertain debt and disinterestedness next. Debt is an corporeality owed for funds borrowed from a banking concern or private lender. The lender agrees to lend funds to the borrower upon a promise by the borrower to pay back the coin likewise as interest on the debt — the interest is usually paid at regular intervals. A business acquires debt in order to use the funds for operating needs. A visitor typically needs hard avails to borrow money from a bank or private lender. A difficult asset is a receivable for a product or service delivered that is recognized on the company'south balance sail and shows a lender the business organization is capable of paying dorsum the loan. If a company is new or doesn't have hard avails it's more than difficult to borrow. Disinterestedness is stock or security representing an buying interest in a company. Put just, it's your ownership in an nugget — such as a company, property, or car — later your debt on that asset is paid. When a concern uses equity financing, information technology sells shares of the company to investors in return for capital letter. To learn more, check out this guide to equity financing. Now that we've divers the debt to equity ratio, nosotros'll take a wait at how to use it. Beneath is the formula to calculate the debt to equity ratio: Here are the 2 elements that make up the formula: Let'south say a software company is applying for funding and needs to calculate its debt to equity ratio. Its total liabilities are $300,000 and shareholders' disinterestedness is $250,000. Here's what the debt to equity ratio would expect like for the company: Debt to equity ratio = 300,000 / 250,000 Debt to equity ratio = ane.ii With a debt to equity ratio of ane.two, investing is less risky for the lenders considering the business is non highly leveraged — meaning information technology isn't primarily financed with debt. A good debt to equity ratio is effectually i to 1.5. Nevertheless, the ideal debt to equity ratio will vary depending on the manufacture because some industries use more debt financing than others. Upper-case letter-intensive industries similar the fiscal and manufacturing industries often have higher ratios that can be greater than 2. A high debt to equity ratio indicates a business uses debt to finance its growth. Companies that invest large amounts of money in assets and operations (capital intensive companies) often accept a higher debt to equity ratio. For lenders and investors, a high ratio means a riskier investment considering the business might not be able to produce enough money to repay its debts. If a debt to equity ratio is lower — closer to nada — this often means the business hasn't relied on borrowing to finance operations. Investors are unlikely to invest in a company with a very low ratio considering the business isn't realizing the potential profit or value it could proceeds past borrowing and increasing operations. Businesses with good debt to disinterestedness ratios are those that fall inside the standard range for their industries. These companies are likely in a flow of positive growth supported past counterbalanced financing from both debt lenders and disinterestedness shareholders. Although a company with a good debt to disinterestedness ratio looks good on paper financially, information technology's important to understand that this financial metric is a snapshot that doesn't tell the entire story of how a business is using capital every bit a tool to scale. And then, don't get too comfy when this number is positive. Instead, turn your attending to your long-term debt to equity ratio as this has an impact on your business's fiscal wellness, too. Consider funding whatever long-term growth plans with long-term debt rather than curt-term financing in order to stabilize your pecuniary picture. A negative debt to equity ratio occurs when a company has interest rates on its debts that are greater than the return on investment. Negative debt to equity ratio can also be a effect of a company that has a negative net worth. Companies that experience a negative debt to equity ratio may be seen as risky to analysts, lenders, and investors considering this debt is a sign of financial instability. A company can feel a negative debt to equity ratio for a number of reasons, including: When any of these situations occur, they could signal a sign of financial distress to shareholders, investors, and creditors. If your business has a negative debt to equity ratio, you might have a difficult time finding financing in the time to come due to the amount of debt you already use to fund your company. The respond to this is not to jump into more equity financing as this can crusade issues with the operations of your business concern. Extending more disinterestedness to new shareholders tin can cause your company to pursue a different direction as a contingency of accepting their financing. Instead, if you want to lower your debt to equity ratio, y'all might prioritize repaying the debt yous owe before growing your concern further. Check CSIMarket for debt to disinterestedness ratio standards in your industry to come across how yours compares to those of other businesses. The long-term debt to disinterestedness ratio shows how much of a business' assets are financed by long-term financial obligations, such equally loans. To calculate long-term debt to equity ratio, divide long-term debt by shareholders' equity. As we covered in a higher place, shareholders' equity is full assets minus total liabilities. All the same, this is non the aforementioned value equally full avails minus total debt considering the payment terms of the debt should also exist taken into account when assessing the overall financial health of a company. Brusque-term debt consists of liabilities that will be paid in nether a yr. Long-term debt consists of liabilities that will take a twelvemonth or more to mature. Permit's walk through an example. Company A has $2 million in short-term debt and $1 1000000 in long-term debt. Company B has $1 one thousand thousand in short-term debt and $2 1000000 in long-term debt. Both companies have $3 million in debt and $3.1 million in shareholder equity giving them both a debt to equity ratio of 1.03. Nonetheless, because short-term debt is renewed more frequently, having greater short-term debt compared to long-term debt is considered risky, specially with fluctuating interest rates. With this in mind, Company B would be considered less risky because it has more long-term debt, which is considered more stable. Here's a reference to help y'all remember the long-term debt to disinterestedness ratio formula. Examples of long-term debt include mortgages, bonds, and bank debt. Simply like the standard debt to equity ratio, investing in a business is riskier if it has a high ratio. Debt tin can be a 4-alphabetic character word to modest and scaling businesses, but information technology doesn't have to be. When used correctly, debt can show investors and lenders that you're using the resources available to your business in social club to realize a positive render on investment. The debt to equity ratio is a valuable tool for entrepreneurs and investors, and it shows how much a business relies on debt to finance its purchases and concern activities in relation to the equity it uses for the same purposes. This ratio is fluid beyond industries, so check the standards for your company as you begin financing large projects and growth strategies. Editor's note: This post was oriCompaginally published in October 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness. 
Debt to Equity Ratio
Why Is Debt to Equity Ratio Of import?
What is debt?
What is equity?
Debt to Equity Ratio Formula

Debt to Disinterestedness Ratio Case
What is a good debt to equity ratio?
What Should Businesses with Good Debt to Equity Ratios Exercise Adjacent?
What is a negative debt to equity ratio?
What Should Yous Do If You lot Take Negative Debt to Equity Ratio?
Long-term Debt to Equity Ratio

Using Debt and Equity to Calibration Your Business


Originally published Oct 27, 2021 4:00:00 PM, updated February 04 2022
Source: https://blog.hubspot.com/sales/debt-equity-ratio